Pre-Calculus
Algebra
Arithmetic Operations
Arithmetic Operations
Exponents and Radicals
Exponents and Radicals
Factoring Special Polynomials
Factoring Special Polynomials
Binomial Theorem
Quadratic Formula
If 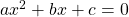 , then
, then 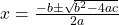
Inequalities and Absolute Values
| If a < b and b < c, the a < c. | If a < b, then a+c < b+c. |
| If a < b and c > 0, then ca < cb. | If a < b and c < 0, then ca > cb. |
| If a > 0, then | |x|=a means x=a or x=-a |
| |x| < a means -a < x < a |
| |x| > a means x > a or x < -a |
Inequalities and Absolute ValuesGeometry
Geometric Formulas
Formulas for area A, circumference C, and volume V
| Triangle | 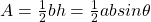 where where 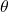 is the angle made by a and b. Also, b is the base of the triangle and h is the height of the triangle. is the angle made by a and b. Also, b is the base of the triangle and h is the height of the triangle. |
| Circle | 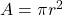
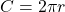 |
| Sector of Circle | 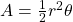
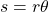
(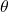 in radians) in radians) |
| Sphere | 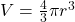
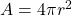 |
| Cylinder | 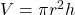 |
| Cone | 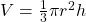
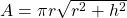 |
Formulas for area A, circumference C, and volume VDistance and Midpoint Formulas
| Distance between points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2): | 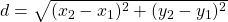 |
| Midpoint between points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2): | 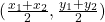 |
Distance and Midpoint FormulasProperties of Lines
| Slope of a line through points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2): | 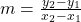 |
| Point-slope equation of a line through point (x1,y1) with slope m: | 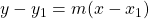 |
| Slope-intercept equation of a line with slope m and y-intercept b: | 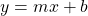 |
Properties of LinesCircle Equation
| The equation of a circle with center at (h,k) and radius r: | 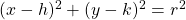 |
Circle EquationTrigonometry
Angle Measurement
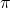 radians =
radians = 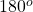
Right Angle Trigonometry
Right Angle Trigonometry
A nice thing to think of is SohCahToa. S(in)o(pp)h(yp)C(osine)a(dj)h(yp)T(angent)o(opp)a(adj)
Fundamental Identities
Fundamental Identities
The Law of Sines
| For a triangle where a is the side opposite of angle A, b is the side opposite of angle B, and c is the side opposite of angle C: |
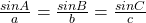 |
The Law of SinesThe Law of Cosines
| For a triangle where a is the side opposite of angle A, b is the side opposite of angle B, and c is the side opposite of angle C: |
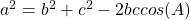 |
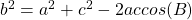 |
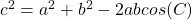 |
The Law of CosinesAddition and Subtraction Formulas
Addition and Subtraction Formulas
Double-Angle Formulas
Double-Angle Formulas
Half-Angle Formulas
Half-Angle Formulas
![]() , then
, then ![]()
![]() radians =
radians = ![]()